.jpg) Methanal (formaldehyde) is usually used as an aqueous solution containing 37% (w/w) methanal, known as formalin. It contains a small amount of methanol and an inhibitor (often an ethenyl (vinyl) polymer) to prevent the aldehyde from forming long chain polymers on storage.
Methanal (formaldehyde) is usually used as an aqueous solution containing 37% (w/w) methanal, known as formalin. It contains a small amount of methanol and an inhibitor (often an ethenyl (vinyl) polymer) to prevent the aldehyde from forming long chain polymers on storage.
Uses of methanal (formaldehyde)
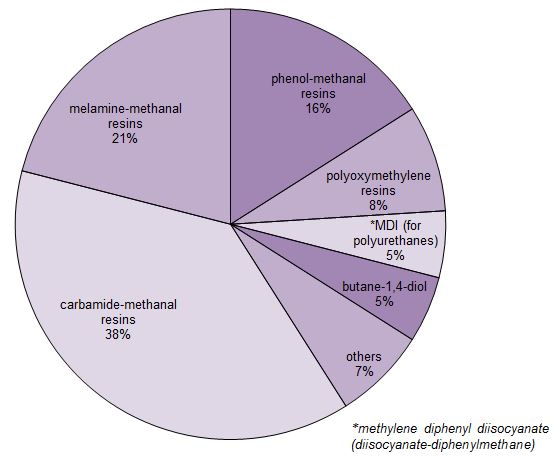
By far the largest use of methanal is in the production of the methanal resins. The principal ones are made from methanal and phenol from methanal and carbamide (urea)and from methanal and melamine.
Figure 1 Uses of methanal.
Data for 2015, MMSA, 2016
Other polymers, based on the polymerization of methanal are discussed below.
Annual production of methanal (formaldehyde), as formalin1
| World | 41 million tonnes2 |
| China | 21 million tonnes |
| US | 5.9 million tonnes |
| Russia | 2.7 million tonnes |
| Germany | 2.1 million tonnes |
1. Data for 2012, Merchant and Research Consulting, 2016
2. Expected to be more than 52 million tonnes in 2017
Manufacture of methanal (formaldehyde)
Most methanal is produced from methanol by a process that involves both dehydrogenation and oxidation:
.jpg)
A mixture of methanol vapour and air at ca 1000 K and just above atmospheric pressure is passed over a catalyst of finely divided silver or molybdenum(VI) oxide on an inert support.
The resulting methanal is absorbed in water. The byproduct, hydrogen, is used as a fuel for the process.
Polyoxymethylene resins (polyacetal resins)
The polymerization of anhydrous methanal leads to the formation of the polyoxymethylene (or acetal) resins, which are thermoplastics.
They are either made as a homopolymer, to which ethanoic acid is added to terminate the chains:
.jpg)
Alternatively, they are produced as a co-polymer, with epoxyethane:
.jpg)
Both the homopolymer and co-polymer are very tough and resistant to abrasion. They are used, instead of metals, in, for example, bearings and gears and in plumbing.
| Figure 2 The photograph shows the black casing that holds a fuel filter for an Audi car and on the right it shows how the filter fits into the fuel system. The plastic used to make the casing, as well as being suitably strong when moulded into the required shape, must also have good electrical conductivity. Fuel moving through the filter could cause the build up of an electrostatic charge that could lead to sparking unless the casing can safely conduct away the charge. The casing is a composite made from a polyoxymethylene resin, which has carbon nanotubes dispersed throughout the resin matrix to enhance its electrical conductivity. By kind permission of BASF. |
.jpg) |
Date last amended: 18th November 2016